chmod Command in Linux/Unix
Assigning file permission is another security feature provided by Linux/Unix.
Why File permission??
File permission helps you to restrict the access of you files from others (Group member and other user) in Multi-user environment. By using permissions you can specify who can interact with your files and how (read,write or execute).
Linux/Unix has three user classes
1. User (u) : The owner of the file.
2. Group (g) : The group that the owner belongs to. This can be useful when you are involve in a project , and group member require to access file which other can't.
3. Others (o) : Everyone else.
Access Permission In Linux/Unix
1. Read (r)
Files : If r bit is set for file then file is Readable.
Directory : If r bit is set for directory then you can list the content of directory .
2. Write (w)
Files : If w bit is set you can modify that file i,e write data to the file , delete data from file.
Directory : If w bit is set for directory then you are permitted to create or remove files in it. if w bit is not set , you can't create , copy or delete a files in it.
3. Execute (x)
Files : If x bit is set you can Execute that file i,e Executing any shell script file or c/c++file.
Directory : For directory it is also refer as search bit , It allows to search for a sub- directory and files in a directory if search bit is set. If directory doesn't have execute permission , then it can't searched for the name of the next directory.
File Permission
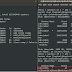
You can use ls -l command to list content of current directory with their access permissions.
For file abc.lst
1. It belongs to user "sandeep"
2. It belongs to a group "sandeep"
Lets closely interpret the meaning of first field
chmod
chmod command is used to change the permission of files and directory.
Syntax
chmod mode file/directory
Permission can be changed in two ways
1. Symbolic mode
2. Numeric mode
u-user + assign permission r read
g-group - Remove permission w write
o-others = Absolute permission x execute
a-all(ugo)
Assigning file permission is another security feature provided by Linux/Unix.
Why File permission??
File permission helps you to restrict the access of you files from others (Group member and other user) in Multi-user environment. By using permissions you can specify who can interact with your files and how (read,write or execute).
Linux/Unix has three user classes
1. User (u) : The owner of the file.
2. Group (g) : The group that the owner belongs to. This can be useful when you are involve in a project , and group member require to access file which other can't.
3. Others (o) : Everyone else.
Access Permission In Linux/Unix
1. Read (r)
Files : If r bit is set for file then file is Readable.
Directory : If r bit is set for directory then you can list the content of directory .
2. Write (w)
Files : If w bit is set you can modify that file i,e write data to the file , delete data from file.
Directory : If w bit is set for directory then you are permitted to create or remove files in it. if w bit is not set , you can't create , copy or delete a files in it.
3. Execute (x)
Files : If x bit is set you can Execute that file i,e Executing any shell script file or c/c++file.
Directory : For directory it is also refer as search bit , It allows to search for a sub- directory and files in a directory if search bit is set. If directory doesn't have execute permission , then it can't searched for the name of the next directory.
File Permission
You can use ls -l command to list content of current directory with their access permissions.
For file abc.lst
1. It belongs to user "sandeep"
2. It belongs to a group "sandeep"
Lets closely interpret the meaning of first field
chmod
chmod command is used to change the permission of files and directory.
Syntax
chmod mode file/directory
Permission can be changed in two ways
1. Symbolic mode
2. Numeric mode
Symbolic mode
category operation Permissionu-user + assign permission r read
g-group - Remove permission w write
o-others = Absolute permission x execute
a-all(ugo)
1. Give read permission to all users and remove all other permission.
2. Give write and execute permission to user and execute permission to group members.
3. Remove execute permission from both user and group.
Numeric Mode
Pemission in Numeric mode is represented by
1. Read permission - 4 ( 100)
2. Write Permission - 2 ( 010)
3. Execute permission - 1 ( 001)
4. No permission - 0 ( 000)
If command is like this chmod 754 abc.lst , then this means
1. 7 - 111 - rwx - All permission for user
2. 5 - 101 - r-x - Readable and executable by group.
3. 4 - 100 - r-- - Only Readable by others
Different combination of Permission
Binary octal permission Significance
000 0 --- No permission
001 1 --x Executable Only
010 2 -w- Writable only
011 3 -wx Writable and Executable
100 4 r-- Readable only
101 5 r-x Readable and Executable
110 6 rw- Readable and writable
111 7 rwx Readable,Writable and Executable
*They are also Known as absolute permission. In this you don't have to remember what a file's current permission , you have to set all permission explicitly.
Example
Suppose we have file abc.lst and it has permission -rw-r--r-- i,e 644 in octal.
1. Give read permission to all users and remove all other permission.
2. Give write and execute permission to user and execute permission to group members and remove all other permission.
3. Set all Permission for all users.
Using chmod Recursively
chmod can be used to apply same permission for directory and all other sub-directory with in it.This can be done using -R option
$ chmod -R 755 dir_name
* This will apply 755 permission to all files and sub-directory with in dir_name directory.
If You Liked This Post Please Take a Time To Share This Post















well done bro!! great job!!:) this was the best tutorial for chmod i hv seen..
ReplyDeleteAmazing/Interesting Facts about Indian Railways https://goo.gl/kmR3M6
ReplyDeleteIts a very informative and amazing blog post site. we will wait for your next blog post.
ReplyDeletehttps://www.lovingparents.in/kids/kids-5-12-years/7-common-childhood-illnesses-and-their-treatments/
Thanks for the post. it was worth reading.
ReplyDeleteLinux Classes in Pune