 When doing any moderate to advanced networking, you are likely to have to deal with subnetting. While some people have an ability to do the binary math in their head to figure out the correct subnet-mask, some may find it difficult to calculate, for them Ipcalc is a tool in Linux which help them to calculate no. of subnets, subnetting mask and other Ip addressing related stuffs.
When doing any moderate to advanced networking, you are likely to have to deal with subnetting. While some people have an ability to do the binary math in their head to figure out the correct subnet-mask, some may find it difficult to calculate, for them Ipcalc is a tool in Linux which help them to calculate no. of subnets, subnetting mask and other Ip addressing related stuffs.Ipcalc takes an IP address and netmask and calculates the resulting broadcast, network, Cisco wildcard mask, and host range. By giving a second netmask, you can design subnets and supernets. It is also intended to be a teaching tool and presents the subnetting results as easy-to-understand binary values.
How to Install Ipcalc
To install Ipcalc in Ubuntu or debian based distros, open terminal ( Ctrl + Alt + t) and run the following command$ sudo apt-get install ipcalc
How to use Ipcalc
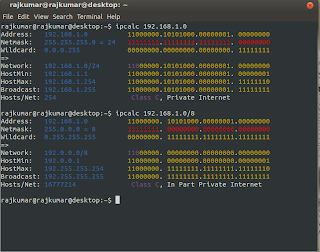
1. Know everything about the network address$ ipcalc 192.168.1.0 Address: 192.168.1.0 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 = 24 11111111.11111111.11111111. 00000000 Wildcard: 0.0.0.255 00000000.00000000.00000000. 11111111 => Network: 192.168.1.0/24 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000 HostMin: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000001 HostMax: 192.168.1.254 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11111110 Broadcast: 192.168.1.255 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11111111 Hosts/Net: 254 Class C, Private Internet
2. Specify Ip address using CIDR representation
$ ipcalc 192.168.1.0/28 Address: 192.168.1.0 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 0000 Netmask: 255.255.255.240 = 28 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111 0000 Wildcard: 0.0.0.15 00000000.00000000.00000000.0000 1111 => Network: 192.168.1.0/28 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 0000 HostMin: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 0001 HostMax: 192.168.1.14 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 1110 Broadcast: 192.168.1.15 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 1111 Hosts/Net: 14 Class C, Private Internet
3. Suppress binary output
$ ipcalc -b 192.168.1.0/12 Address: 192.168.1.0 Netmask: 255.240.0.0 = 12 Wildcard: 0.15.255.255 => Network: 192.160.0.0/12 HostMin: 192.160.0.1 HostMax: 192.175.255.254 Broadcast: 192.175.255.255 Hosts/Net: 1048574 Class C, In Part Private Internet
4. Calculate single subnet with 10 host.
$ ipcalc 192.168.1.0 --s 10 Address: 192.168.1.0 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 = 24 11111111.11111111.11111111. 00000000 Wildcard: 0.0.0.255 00000000.00000000.00000000. 11111111 => Network: 192.168.1.0/24 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000 HostMin: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000001 HostMax: 192.168.1.254 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11111110 Broadcast: 192.168.1.255 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11111111 Hosts/Net: 254 Class C, Private Internet 1. Requested size: 10 hosts Netmask: 255.255.255.240 = 28 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111 0000 Network: 192.168.1.0/28 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 0000 HostMin: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 0001 HostMax: 192.168.1.14 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 1110 Broadcast: 192.168.1.15 11000000.10101000.00000001.0000 1111 Hosts/Net: 14 Class C, Private Internet Needed size: 16 addresses. Used network: 192.168.1.0/28 Unused: 192.168.1.16/28 192.168.1.32/27 192.168.1.64/26 192.168.1.128/25
5. You can calculate multiple subnets using single command. Lets say you want to divide 134.1.12.45 in three subnets for total 50 hosts. Specify your network mask and no. of host in each segment.
$ ipcalc 134.1.12.45/20 --s 10 20 20 Address: 134.1.12.45 10000110.00000001.0000 1100.00101101 Netmask: 255.255.240.0 = 20 11111111.11111111.1111 0000.00000000 Wildcard: 0.0.15.255 00000000.00000000.0000 1111.11111111 => Network: 134.1.0.0/20 10000110.00000001.0000 0000.00000000 HostMin: 134.1.0.1 10000110.00000001.0000 0000.00000001 HostMax: 134.1.15.254 10000110.00000001.0000 1111.11111110 Broadcast: 134.1.15.255 10000110.00000001.0000 1111.11111111 Hosts/Net: 4094 Class B 1. Requested size: 10 hosts Netmask: 255.255.255.240 = 28 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111 0000 Network: 134.1.0.64/28 10000110.00000001.00000000.0100 0000 HostMin: 134.1.0.65 10000110.00000001.00000000.0100 0001 HostMax: 134.1.0.78 10000110.00000001.00000000.0100 1110 Broadcast: 134.1.0.79 10000110.00000001.00000000.0100 1111 Hosts/Net: 14 Class B 2. Requested size: 20 hosts Netmask: 255.255.255.224 = 27 11111111.11111111.11111111.111 00000 Network: 134.1.0.0/27 10000110.00000001.00000000.000 00000 HostMin: 134.1.0.1 10000110.00000001.00000000.000 00001 HostMax: 134.1.0.30 10000110.00000001.00000000.000 11110 Broadcast: 134.1.0.31 10000110.00000001.00000000.000 11111 Hosts/Net: 30 Class B 3. Requested size: 20 hosts Netmask: 255.255.255.224 = 27 11111111.11111111.11111111.111 00000 Network: 134.1.0.32/27 10000110.00000001.00000000.001 00000 HostMin: 134.1.0.33 10000110.00000001.00000000.001 00001 HostMax: 134.1.0.62 10000110.00000001.00000000.001 11110 Broadcast: 134.1.0.63 10000110.00000001.00000000.001 11111 Hosts/Net: 30 Class B Needed size: 80 addresses. Used network: 134.1.0.0/25 Unused: 134.1.0.80/28 134.1.0.96/27 134.1.0.128/25 134.1.1.0/24 134.1.2.0/23 134.1.4.0/22 134.1.8.0/21
6. Display result as HTML
$ ipcalc 134.1.12.45/20 --h
7. To know more about Ipcalc, please refer man page or use help command
$ man ipcalc $ ipcalc --help
That's it. Hope you enjoyed the post.
If You Liked This Post Please Take a Time To Share This Post





ipcalc takes an IP address calculator and netmask and calculates the resulting broadcast, network, Cisco wildcard mask, and host range. By giving a second netmask, you can design subnets and supernets. It is also intended to be a teaching tool and presents the subnetting results as easy-to-understand binary values.
ReplyDeleteEnter your netmask(s) in CIDR notation (/25) or dotted decimals (255.255.255.0). Inverse netmasks are recognized. If you omit the netmask ipcalc uses the default netmask for the class of your network.
I do not run an ubuntu derivative, therefore apt-get is useless to me.
ReplyDeletewhere can I download a tar file?
thank you
nice information..Class C IP tool is one of the best tool .class c ip checker
ReplyDeleteVery nice information.This is really a nice blog..very informative & very interesting. Use this tool to identify site networks.class c ip checker
ReplyDeleteIn my opinion, great content is above all. So focusing on creating good quality content is the solution.
ReplyDeleteMelbourne SEO Services
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletehttps://saglamproxy.com
ReplyDeletemetin2 proxy
proxy satın al
knight online proxy
mobil proxy satın al
KPS
สล็อต pg ทาง เข้า slot ทาง เข้า เว็บแตกง่าย สมัครเล่นวันนี้แจกฟรี ยินดีต้อนรับทุนท่านไปสู่จักรวาลที่สุด PG SLOT แสนจะท้าทายที่พร้อมจะพาคุณไปเปิดประตูสู่ความร่ำรวยอย่างมากมาย
ReplyDeleteВаши комментарии всегда являются источником поддержки и мотивации. Только что попробовал кликов в секунду на bestclicktest, и он затягивает! Отличный способ измерить и улучшить скорость нажатия.
ReplyDeleteAppreciate the effort! This was a great post. Learn game-winning techniques from the T-Rex Game profile. The T-Rex Game is the perfect way to test your focus. Stay alert, time your jumps and ducks perfectly, and aim for a new high score.
ReplyDelete